Deep Analysis of “Rule-Based Chatbots”
Our mission is to make your business better through technology

Table of Contents
Deep Analysis of Rule-Based Chatbots explores how rule based chatbots operate using predefined rules, decision trees, and structured responses. These chatbots follow fixed patterns to deliver accurate, predictable answers, making them ideal for handling FAQs, guided support, and controlled workflows. This introduction highlights their strengths, limitations, and real-world applications, helping businesses understand where these traditional chatbot systems excel and how they can be optimized for consistent customer interactions.
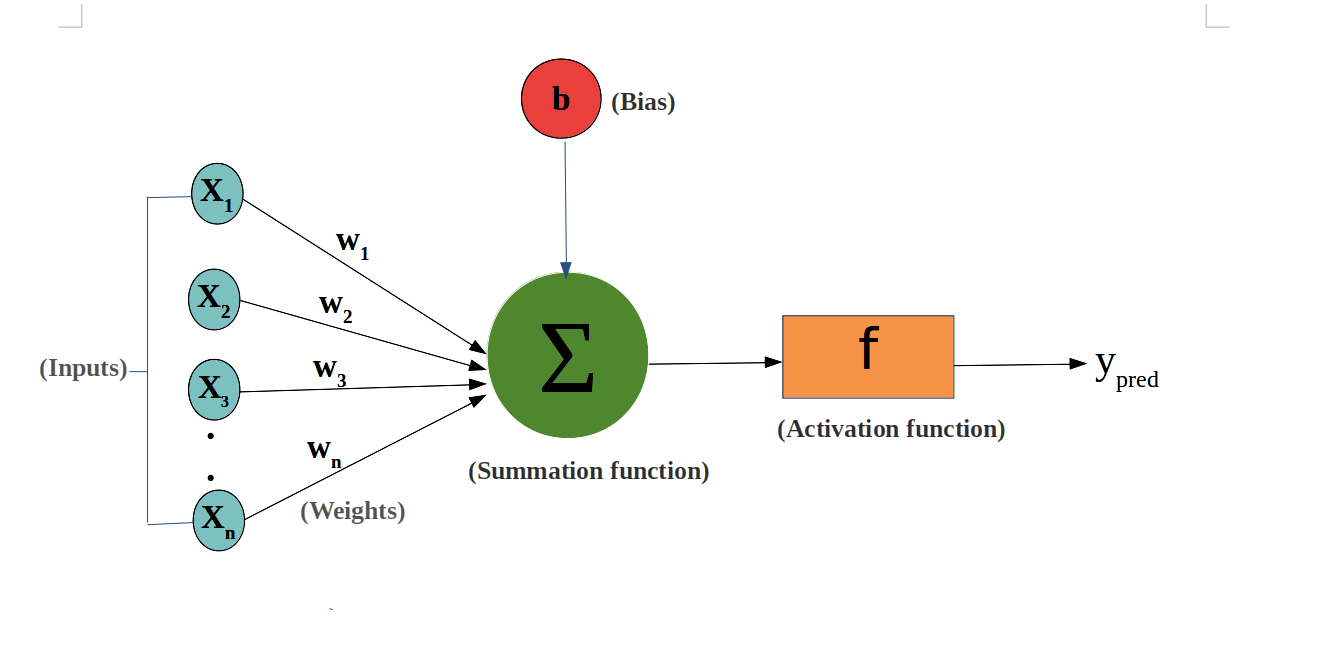
Core Architecture
Rule-based chatbots rely on ‘deterministic workflows’ built by developers. Their structure includes:
Input Parsing
- Matches user inputs to predefined keywords or patterns (e.g., regex, exact phrases).
- Example: A user types “Check balance” → triggers the “account balance” rule.
Decision Tree
- A flowchart-like logic where each user input branches to a predefined response.
Example:
If the user says “reset password” → Ask for email verification.
If the user says “track order” → Request order ID.
Static Knowledge Base
- Limited to hardcoded data (e.g., FAQs, product catalogs).
- Cannot infer or learn from new data outside its rules.
Response Templates
- Prewritten answers mapped to specific triggers (e.g., “Your order status is: [status].”).
Rule-Based Chatbots Key Characteristics
Deterministic Behavior
- Always produces the same output for identical inputs.
- No randomness or adaptability (e.g., responds to “Help” with the same menu every time).
No Learning Capability
- Cannot improve over time or handle inputs outside its rule set.
Limited Context Awareness
- Struggles with follow-up questions unless explicitly programmed (e.g., “What about my other order?”).
Low Complexity
- Ideal for narrow, repetitive tasks (e.g., password resets, booking confirmations).
Use Cases

Rule-based chatbots excel in scenarios with predictable interactions:
Customer Support
- Answering FAQs (e.g., “What’s your return policy?”).
- Guiding users through fixed processes (e.g., “Click here to reset your password”).
Appointment Scheduling
- Booking slots using calendar rules (e.g., “Choose a date between Monday-Friday”).
Surveys and Forms
- Collecting structured data (e.g., “Enter your email address”).
Basic E-commerce
- Order tracking (e.g., “Your package will arrive on [date]”).
Advantages
Predictability:
- Ensures compliance with business rules (e.g., legal disclaimers).Ensures compliance with business rules (e.g., legal disclaimers).
Ease of Development:
- Requires no ML expertise; built using tools like Dialogflow ES, Microsoft Bot Framework, or simple scripting.
Cost-Effective:
- Low computational/resources overhead compared to AI models.
Transparency:
- Easy to audit and debug since logic is explicit.
Limitations
Brittle to Variations:
- Fails if users rephrase questions (e.g., “I forgot my password” vs. “Can’t log in”).
Scalability Issues:
- Adding new rules becomes complex as scenarios grow (e.g., exponential branching).
No Personalisation:
- Cannot tailor responses based on user history (e.g., “Welcome back, [Name]” requires hardcoding).
High Maintenance:
- Requires manual updates for new queries or changing business logic.
Comparison with AI-Driven Chatbots
| Feature | Rule-Based Chatbots | AI-Driven Chatbots |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Rigid, limited to rules | Adapts to unstructured inputs |
| Learning | None | Improves via ML/NLP |
| Complexity | Simple, linear workflows | Handles multi-turn, context-rich dialogues |
| Development Effort | Low (scripting) | High (data training, model tuning) |
| Cost | Low | High (compute/resources) |
| Use Case Fit | Narrow, repetitive tasks | Open-ended, dynamic interactions |
Challenges
Ambiguity Handling
- Struggles with synonyms, typos, or slang (e.g., “PLS HELP!!”* vs. “Assist me”).
User Frustration
- Fails gracefully (e.g., repetitive “I didn’t understand” messages).
Integration Limits
- Limited ability to connect with dynamic APIs or real-time data without custom coding.
Future Evolution
Hybrid Models
- Combining rule-based logic with AI fallbacks (e.g., rules for compliance, AI for open-ended queries).
Enhanced NLP Integration
- Using lightweight NLP to parse inputs while retaining rule-based responses.
Low-Code Platforms
- Tools like Zapier or Tars enable non-developers to build rule-based bots.
Real-World Examples
Banking:
- Bots that check account balances only when users type “Balance” or “Current funds.”
Healthcare:
- Symptom-checker bots guiding users through yes/no questionnaires.
Retail:
- FAQ bots answering “Where is my order?” with tracking links.
Conclusion
Rule-based chatbots are foundational tools for automating simple, repetitive tasks with high reliability. While they lack the sophistication of AI-driven agents, their transparency, low cost, and ease of deployment make them ideal for businesses with narrow, well-defined use cases. However, as user expectations grow, hybrid approaches (rules + AI) are becoming critical to balance efficiency and flexibility
Share this :